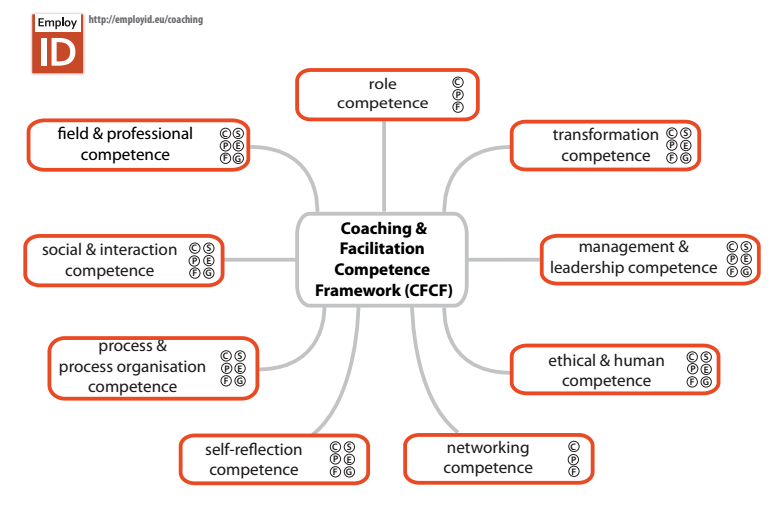
At the moment there is a team in EmployID working on a competence framework that tries to make competences, skills, abilities and knowledge visible that is needed for coaching and faciliation. This competence framework supports trainings for EmployID Academy as well as EmployID trainings for PES.
Clearly for peer coaching there are less skills, abilities, knowledge needed as for individual coaching, since in peer coaching there is no need of a professional coach. The process is lead by peers/ collegues.
Still there are some things all peer coaching participants should be able, “trained” at or at least made aware off to improve these skills during their practice within the peer coaching groups.
This is a quick an incomplete overview!
Development competence
This term is derived from an unpublished paper of two EmployID consortium members. For peer coaching it means basically that there is a need of being able to develop in certain ways.
- peer coaching and self-coaching training: This is of course needed to learn about the peer coaching concept, the background and to have the possibility to “try out” and learn within the process. The peer coaching OOC is one possibility to get an overview and to “get going”. Other possibilities could be on-site training, workshops etc.
- practical development
- emotional development
- emotional regulation
- emotional consciousness
- cognitive development
- meta-cognitive skills
- problem solving
- meta-cognitive skills
Management and leading competence
These competences focuses on management and leading within coaching and facilitation. For peer coaching it is mainly on managing and organization of a intervision group and on progress.
- (change) management skills
- managing progress and accountability
- management & organization
Ethical and human competence
This is a very important point for all coaching and facilitation activities. For peer coaching, the following is important:
- idea of man: This rests upon Carl Rogers humanistic or client-centered approach. The idea of men there is that the person who searched for help has already everything in it to solve the problem, since he is the expert on the situation and only he can analyze the problem correct to find fitting solutions. This is so important, because it makes clear, that to understand the problem situation, there is much need of listening and asking questions.
- meeting ethical guidelines and professional standards: In coaching trust is a very important issue. To develop trust there needs to be clear rules and transparency on the way of working. Also, concerning professionalism in coaching, the associations take much value on that.
- sense of responsibilty / accountability
- non-judgemental
Networking competence
- …
Self-reflection competence
- awareness
- context (person/work/organization) awareness
- group dynamic skills/awareness
- realistic perception of oneself: peer coaching can be a very helpful instrument to learn on oneselfs perception and how others see you.
- reflection/ self-reflection
Process and process-organization competence
- coaching approach
- basics of the coaching process, the procedure of coaching
- goal and need orientation
- planning and goal setting
- transfer & implementation
- organizsational skills
- creating awareness
- moderating the process
Social and interaction competence
- assertiveness
- observation
- lateral thinking
- collaborativeness
- supporting the learning of others
- facilitation learning & results
- resource orientation
- solution/ resource oriented interventions
- inner vision and future work
- solution/ resource oriented interventions
- empathy
- compassion
- establishing trust and initmacy with client/ relationship building
- communication skills
- active listening
- direct communication:
- (effective) feedback
- summarising: Summarizing what was said by the client in own words and asking, if that was understood correctly.
- powerful questioning
- reflective questioning
- meta-communication
- ambiguity tolerance
Field- and professional competence
- experience
- basic understanding of business administration (depending on field)
Role competence
- Roles of peer coaching (see peer coaching concepts)
(EmployID WP 8, 2014)
Resources
EmployID (2014) Coaching to Facilitation Competence Framework. (not published yet; deliverable for WP 8) based on different sources.
Resources