Peer coaching comes from Supervision, where an expert works with one person or a group on their cases at work. It is often used for reflection of counsellors, coaches, educators.
Characteristics of peer coaching
There a certain characteristics on intervision you need to understand:
- group of equal rank
The group that does peer coaching is of equal rank. That does not mean, that persons in the group can be differently qualified, but it means, that everyone in the group may bring in his problem equally and no one of the is a professional coach who leads the group or process.
- common professional focus
Another thing is the professional focus. Usually there is a common professional interest. People in the group have a common objective, because of maybe the same background.
- target-oriented process
The process is target-oriented, meaning is about a solution-focused exchange to find one or more solutions that can be transferred into work afterwards.
- mutualy defined structure
There is a mutually defined structure that supports the peer coaching process (the main structure will be provided to you in this OOC).
- volunatiness, liability
Peer coaching should be voluntary, but within the group there is a need of liability to take part actively and feel responsible for the processes.
- idea of „giving and taking“
There is the idea of “giving and taking”, meaning that you learn from each other and help each other.
- counsel without fee
The peer coaching is without fee, because there is no professional needed, there are trademarked concepts. (Lippmann 2009, pp. 17-19)
Resource peer coaching model
This guide is meant to help organizing and perform peer coaching with other PES practitoners in order to strengthen resources and responsibility of one’s own.
In the figure below (figure 1) the phases in coaching are described on the macro-level:
- the initial phase,
- the main phase and
- the final phase.
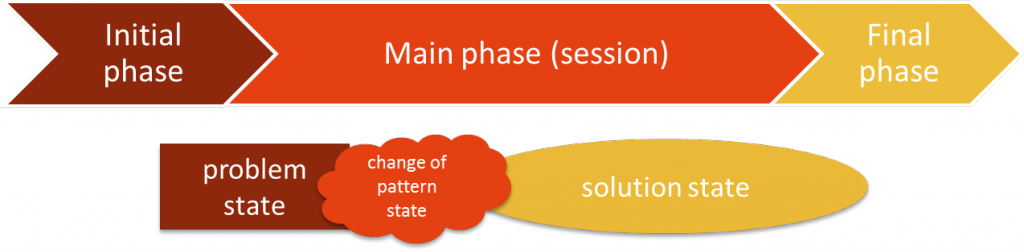
The initial phase is where the peer coaching is organized and structured and to sort out what problems need to be solved. In the main phase the peer coaching process starts to find a solution for the given problem. The final phase is for making plans and giving feedback on the coaching process (there can be more than one coaching process, more than one “main phase”). Below the described phases there are three fields with “problem”, “change of pattern (state)” and “solution”. This is the meso-level of this peer coaching model. First the problem is given, then there is a need to change the pattern state: change your feelings, thoughts, physiology and behavior in order to concentrate on the solution. The peer coaching for PES practitioners is solution-oriented, meaning simply, there is not much time spent analyzing the problem, but focusing on possible solutions and further steps.
The actual coaching process on the micro-level is devided in:
- start, roles, collection of problems, selection
- problem & situation
- vision, resources
- collecting resources
- setting goals
- solutions & next steps
- feedback
These steps will be described in more detail when going into the different peer coaching models (concept I and concept II).
Resources
Berg, Thomas E. & Berninger-Schäfer, Elke (2010). Die Kollegiale Coaching Konferenz. Stuttgart: Boorberg Verlag.
Berninger-Schäfer, Elke (2011). Orientierung im Coaching. Stuttgart: Boorberg Verlag.
Lippmann, Eric (2009). Intervision. Kollegiales Coaching professionell gestalten. Heidelberg: Springer Medizin Verlag.
Wolf, Carmen (2014). EmployID: resource intervision model I & II. Draft (2014, August 15)

0 responses on "*Background"